http://localhost:8080/modeshape-webdav/repositoryName/workspaceName/pathInWorkspace
The ModeShape kit for Wildfly includes a WebDAV interface that clients can use to access, create, update, and delete update nt:file and nt:folder nodes in the repositories, treating these nodes as if they were simply files and folders on a network file system. Many applications and operating systems are WebDAV clients and can be used with ModeShape. For example, you can mount a repository (or parts of it) as a network drive on most operating systems, and then upload or download files and folders using standard OS operations and graphical tools. All ModeShape repositories can be accessed, and authentication is done using the ModeShape 'connect' role (although this can be customized).
The WebDAV service is packaged as a WAR file and is automatically deployed when the ModeShape kit is installed. Simply undeploy it if it is not needed.
The rest of this page describes connecting to the WebDAV service and advanced configuration.
Connecting to the repository with WebDAV
The WebDAV service is available on your Wildfly instance at the URL:
where
-
repositoryName is the (required) name of the repository you want to connect to
-
workspaceName is the (required) name of the workspace to be accessed
-
pathInWorkspace is the JCR path to the top-level nt:folder (or nt:file) node to be accessed
For example, the following images shows how to use the Finder on OS X to connect to the "default" workspace in the "artifacts" sample repository included by default in the ModeShape installation.
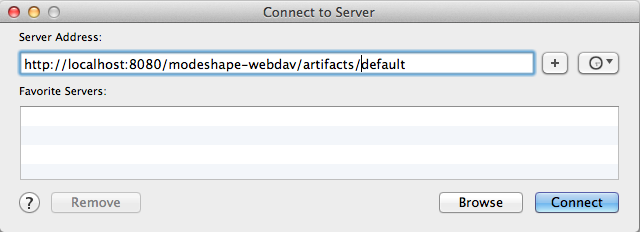
Connecting to a repository over WebDAV
Once connected, your operating system or WebDAV client can simply access the content of the repository as if it were just a regular file system.
Using the file system to navigate repository content
Configuring the ModeShape WebDAV Server
The ModeShape WebDAV server is deployed as a WAR and configured mostly through its web configuration files located within the deployment (at standalone/deployments/modeshape-webdav.war).
The WEB-INF/web.xml defines several parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
Value |
|
org.modeshape.web.jcr.REPOSITORY_PROVIDER |
The fully-qualified name of the class that implements the org.modeshape.web.jcr.spi.RepositoryProvider interface. Unless you are using the ModeShape WebDAV server to connect to a different JCR implementation, this should never change. |
org.modeshape.web.jcr.spi.FactoryRepositoryProvider |
|
org.modeshape.jcr.URL |
This parameter, specific to the FactoryRepositoryProvider implementation, specifies the JNDI URL of the ModeShape Repositories implementation. |
jndi:jcr |
|
org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.CONTENT_MAPPER_CLASS_NAME |
The fully-qualified name of the class that implements the org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.ContentMapper interface, which is responsible for mapping content nodes to WebDAV responses. The DefaultContentMapper implementation maps nodes with type nt:folder and nt:file to WebDAV folders and files, respectively (see other parameters). You can provide your own implementation to map WebDAV content to other node content or structures. |
org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.DefaultContentMapper |
|
org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.NEW_FOLDER_PRIMARY_TYPE_NAME |
Each folder created through the WebDAV servlet will be created as a node with this primary node type. |
nt:folder |
|
org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.NEW_RESOURCE_PRIMARY_TYPE_NAME |
Each resource (e.g., file) created through the WebDAV servlet will be created as a node with this primary node type. |
nt:file |
|
org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.NEW_CONTENT_PRIMARY_TYPE_NAME |
Content created through the WebDAV servlet will be created as a node with the primary node type |
nt:resource |
|
org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.RESOURCE_PRIMARY_TYPE_NAMES |
Nodes with any of the primary node types in this comma-delimited list will be exposed to WebDAV clients as file nodes. |
nt:file |
|
org.modeshape.web.jcr.webdav.CONTENT_PRIMARY_TYPE_NAMES |
Nodes with any of the primary node types in this comma-delimited list will be exposed to WebDAV clients as content nodes (that is, nodes that have the content of the files). |
nt:resource, mode:resource |
There are also sections dictate how authentication is to be performed:
<!--
The ModeShape WebDAV implementation leverages the HTTP credentials to for authentication
and authorization within the JCR repository. Unless the repository provides for anonymous
access, it makes no sense to try to log into the JCR repository without credentials, so
this constraint helps lock down the repository.
This should generally not be modified.
-->
<security-constraint>
<display-name>ModeShape WebDAV</display-name>
<web-resource-collection>
<web-resource-name>WebDAV</web-resource-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</web-resource-collection>
<auth-constraint>
<!--
A user must be assigned this role to connect to any JCR repository, in addition to
needing the READONLY or READWRITE roles to actually read or modify the data.
-->
<role-name>connect</role-name>
</auth-constraint>
</security-constraint>
<!--
Any auth-method will work for ModeShape. BASIC is used this example for simplicity.
-->
<login-config>
<auth-method>BASIC</auth-method>
</login-config>
<!--
This must match the role-name in the auth-constraint above.
-->
<security-role>
<role-name>connect</role-name>
</security-role>